No edit summary Tag: Source edit |
m (Updating categories: added Extinct Fauna) |
||
| (13 intermediate revisions by 6 users not shown) | |||
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
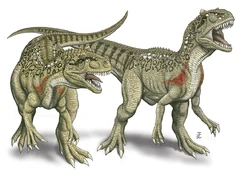
| image_caption = An artist's illustration of a pair of ''Lourinhanosaurus antunesi'' |
| image_caption = An artist's illustration of a pair of ''Lourinhanosaurus antunesi'' |
||
| image_width = 240px |
| image_width = 240px |
||
| − | | regnum = [[ |
+ | | regnum = [[Animalia]] |
| phylum = [[Chordate|Chordata]] |
| phylum = [[Chordate|Chordata]] |
||
| ordo = [[Saurischia]] |
| ordo = [[Saurischia]] |
||
| − | | subordo = [[ |
+ | | subordo = [[Theropoda]] |
| clade = [[Coelurosauria]] |
| clade = [[Coelurosauria]] |
||
| genus = {{Extinct}}'''''Lourinhanosaurus''''' |
| genus = {{Extinct}}'''''Lourinhanosaurus''''' |
||
| Line 17: | Line 17: | ||
| binomial_authority = Mateus, 1998 |
| binomial_authority = Mateus, 1998 |
||
}} |
}} |
||
| − | '''''Lourinhanosaurus''''' (meaning "Lourinhã lizard") was a carnivorous |
+ | '''''Lourinhanosaurus''''' (meaning "Lourinhã lizard") was a carnivorous [[Theropods|theropod]] [[Dinosauria|dinosaur]] that lived during the [[Late Jurassic]] Period (Kimmeridgian/Tithonian) of Portugal. Its first remains were found at Peralta, near Lourinhã, Portugal in 1982, but were not described until 1998, by Portuguese paleontologist Octávio Mateus. |
Its only known species is '''''L. antunesi''''', in honor of Portuguese paleontologist Miguel Telles Antunes. |
Its only known species is '''''L. antunesi''''', in honor of Portuguese paleontologist Miguel Telles Antunes. |
||
==Material== |
==Material== |
||
| − | The holotype (ML370) is a partial skeleton, consisting of the remains of six cervical vertebrae with six ribs, five sacral vertebrae with ribs, 14 caudal vertebrae, eight chevrons, both femora, right tibia and fibula, one metatarsus, two ilia and both pubes and ischia. 32 gastroliths were also found inside the specimen. A femur (ML 555), which was found at Porto das Barcas was assigned to this genus. |
+ | The [[holotype]] (ML370) is a partial skeleton, consisting of the remains of six cervical vertebrae with six ribs, five sacral vertebrae with ribs, 14 caudal vertebrae, eight chevrons, both femora, right tibia and fibula, one metatarsus, two ilia and both pubes and ischia. 32 gastroliths were also found inside the specimen. A femur (ML 555), which was found at Porto das Barcas was assigned to this genus. |
Not far from the Lourinhanosaurus type specimen, a nest, containing around 100 eggs, some of which had fossilized embrious (ML 565) was found. These eggs are about 13 cm long. |
Not far from the Lourinhanosaurus type specimen, a nest, containing around 100 eggs, some of which had fossilized embrious (ML 565) was found. These eggs are about 13 cm long. |
||
==Classification== |
==Classification== |
||
| − | Lourinhanosaurus has puzzled paleontologists: initially, it was considered a primitive member of Allosauroidea. Now, some think it is closely related to the Sinraptoridae (making it the first sinraptorid to be discovered outside of China), while others argue that Lourinhanosaurus is, in fact, a member of the Megalosauroidea. |
+ | Lourinhanosaurus has puzzled paleontologists: initially, it was considered a primitive member of Allosauroidea. Now, some think it is closely related to the Sinraptoridae (making it the first sinraptorid to be discovered outside of China), while others argue that Lourinhanosaurus is, in fact, a member of the Megalosauroidea. Carrano ''et al.'' (2012) even found it to be a coelurosaur. |
[[File:Lourinhanosaurus-skeleton.jpg|thumb|289x289px|The holotype material of L. antunesi.]] |
[[File:Lourinhanosaurus-skeleton.jpg|thumb|289x289px|The holotype material of L. antunesi.]] |
||
==Paleobiology== |
==Paleobiology== |
||
[[File:Lourinhanosaurus embrio.jpg|thumb|220x220px|Fossilized embryonic bones referred to L. antunesi.]] |
[[File:Lourinhanosaurus embrio.jpg|thumb|220x220px|Fossilized embryonic bones referred to L. antunesi.]] |
||
| − | The holotype was estimated at being 4,5 metres long. However, being 4 years when it died, it was a sub-adult. The size of an adult individual was estimated at around 8 metres long, which would make Lourinhanosaurus a big theropod (for Jurassic standards), but still well inside the size range observed in other Jurassic theropods. |
+ | The [[holotype]] was estimated at being 4,5 metres long. However, being 4 years when it died, it was a sub-adult. The size of an adult individual was estimated at around 8 metres long, which would make Lourinhanosaurus a [[Largest Theropods|big theropod]] (for [[Jurassic]] standards), but still well inside the size range observed in other Jurassic [[theropods]]. What is most surprising, however, is the presence of [[Gastroliths]] in association with the Lourinhanosaurus remains. This wouldn't be strange if the animal in question was a herbivore. The fact that these gastroliths were found inside a carnivore made paleontologists really confused. |
| − | What is most surprising, however, is the presence of gastroliths in association with the Lourinhanosaurus remains. This wouldn't be strange if the animal in question was a herbivore. The fact that these gastroliths were found inside a carnivore made paleontologists really confused. |
||
| − | One possible explanation is that Lourinhanosaurus was a specialized hunter, eating , for example, shellfish and crustaceans. At the time, the sea levels were much higher and Europe was more like a giant archipelago, instead of a single big land mass. It is possible that young Lourinhanosaurus lived more in coastal ecosystems and, therefore, would have different food sources, according to their ages. This way, they would not compete with older Lourinhanosaurus and even other predators, such as Allosaurus. |
+ | One possible explanation is that Lourinhanosaurus was a specialized hunter, eating , for example, shellfish and crustaceans. At the time, the sea levels were much higher and Europe was more like a giant archipelago, instead of a single big land mass. It is possible that young Lourinhanosaurus lived more in coastal ecosystems and, therefore, would have different food sources, according to their ages. This way, they would not compete with older Lourinhanosaurus and even other predators, such as [[Allosaurus]]. |
[[File:Lourinhanosaurus at the museum.jpg|thumb|220x220px|Lourinhanosaurus at the Museu da Lourinhã.]] |
[[File:Lourinhanosaurus at the museum.jpg|thumb|220x220px|Lourinhanosaurus at the Museu da Lourinhã.]] |
||
When younger and smaller, Lourinhanosaurus may have frequented coastal environments which were far more extensive in Jurassic Europe. Here they would be able to feed by either hunting smaller dinosaurs or raiding tidal pools for fish and crustaceans, the latter two choices requiring the use of gastroliths. Lourinhanosaurus that survived to adulthood may have grown too large to support themselves by this and switched to a greater reliance upon hunting other dinosaurs, again the two generations avoiding competition with one another for the same resources. |
When younger and smaller, Lourinhanosaurus may have frequented coastal environments which were far more extensive in Jurassic Europe. Here they would be able to feed by either hunting smaller dinosaurs or raiding tidal pools for fish and crustaceans, the latter two choices requiring the use of gastroliths. Lourinhanosaurus that survived to adulthood may have grown too large to support themselves by this and switched to a greater reliance upon hunting other dinosaurs, again the two generations avoiding competition with one another for the same resources. |
||
| − | [[File:Slide6-young-t-rex.jpg|thumb|220x220px|A juvenile Tyrannosaurus rex. (Note the more gracile and slender look of a young T. rex, comparing with an adult, which is far more bulkier). |
+ | [[File:Slide6-young-t-rex.jpg|thumb|220x220px|A juvenile Tyrannosaurus rex. (Note the more gracile and slender look of a young T. rex, comparing with an adult, which is far more bulkier).]] |
| − | This strategy is also seen in Tyrannosaurs. When young, they seem to have been very fast and agile predators, making them suitable to chase down smaller and faster ornithopod dinosaurs. In later life, they grew much bigger and no longer had the agility to hunt these swifter dinosaurs which also no longer offered a sufficient return in calories, so the adults switched to hunting larger and heavier dinosaurs. This niche specialisation also allowed juveniles and adults of the same species to coexist in the same ecosystem without competing with each other for the same food. |
+ | This strategy is also seen in [[Tyrannosaurus|Tyrannosaurs]]. When young, they seem to have been very fast and agile predators, making them suitable to chase down smaller and faster [[Ornithopoda|ornithopod]] dinosaurs. In later life, they grew much bigger and no longer had the agility to hunt these swifter dinosaurs which also no longer offered a sufficient return in calories, so the adults switched to hunting larger and heavier dinosaurs. This niche specialisation also allowed juveniles and adults of the same species to coexist in the same ecosystem without competing with each other for the same food. |
==In popular culture== |
==In popular culture== |
||
| Line 46: | Line 45: | ||
==Gallery== |
==Gallery== |
||
| − | <gallery |
+ | <gallery> |
Screenshot 2020-09-23 at 3.19.50 PM.png |
Screenshot 2020-09-23 at 3.19.50 PM.png |
||
Screenshot 2021-03-09 at 11.21.34 AM.png |
Screenshot 2021-03-09 at 11.21.34 AM.png |
||
| Line 53: | Line 52: | ||
</gallery> |
</gallery> |
||
| + | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| + | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| + | |||
| ⚫ | |||
[[Category:Dinosaurs of Europe]] |
[[Category:Dinosaurs of Europe]] |
||
[[Category:Jurassic dinosaurs]] |
[[Category:Jurassic dinosaurs]] |
||
| + | [[Category:Jurassic Fauna]] |
||
[[Category:Late Jurassic dinosaurs]] |
[[Category:Late Jurassic dinosaurs]] |
||
[[Category:Lourinhã Formation]] |
[[Category:Lourinhã Formation]] |
||
[[Category:Dinosaurs of Portugal]] |
[[Category:Dinosaurs of Portugal]] |
||
[[Category:Taxa named by Octávio Mateus]] |
[[Category:Taxa named by Octávio Mateus]] |
||
| − | [[Category: |
+ | [[Category:1998]] |
| − | [[Category:Jurassic Park |
+ | [[Category:Jurassic Park]] |
| + | [[Category:Mesozoic Fauna]] |
||
| + | [[Category:Kimmeridgian Fauna]] |
||
| + | [[Category:Kimmeridgian Reptiles]] |
||
| + | [[Category:Kimmeridgian Dinosaurs]] |
||
| + | [[Category:Tithonian Fauna]] |
||
| + | [[Category:Tithonian Reptiles]] |
||
| ⚫ | |||
| + | [[Category:Extinct Fauna of Europe]] |
||
| + | [[Category:Extinct fauna of Portugal]] |
||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
Latest revision as of 16:53, 28 February 2024
| Lourinhanosaurus | |
|---|---|
| |
| An artist's illustration of a pair of Lourinhanosaurus antunesi | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Order: | Saurischia |
| Suborder: | Theropoda |
| Genus: | †Lourinhanosaurus Mateus, 1998 |
| Species: | †L. antunesi |
| Binomial name | |
| Lourinhanosaurus antunesi Mateus, 1998 | |
Lourinhanosaurus (meaning "Lourinhã lizard") was a carnivorous theropod dinosaur that lived during the Late Jurassic Period (Kimmeridgian/Tithonian) of Portugal. Its first remains were found at Peralta, near Lourinhã, Portugal in 1982, but were not described until 1998, by Portuguese paleontologist Octávio Mateus.
Its only known species is L. antunesi, in honor of Portuguese paleontologist Miguel Telles Antunes.
Material
The holotype (ML370) is a partial skeleton, consisting of the remains of six cervical vertebrae with six ribs, five sacral vertebrae with ribs, 14 caudal vertebrae, eight chevrons, both femora, right tibia and fibula, one metatarsus, two ilia and both pubes and ischia. 32 gastroliths were also found inside the specimen. A femur (ML 555), which was found at Porto das Barcas was assigned to this genus.
Not far from the Lourinhanosaurus type specimen, a nest, containing around 100 eggs, some of which had fossilized embrious (ML 565) was found. These eggs are about 13 cm long.
Classification
Lourinhanosaurus has puzzled paleontologists: initially, it was considered a primitive member of Allosauroidea. Now, some think it is closely related to the Sinraptoridae (making it the first sinraptorid to be discovered outside of China), while others argue that Lourinhanosaurus is, in fact, a member of the Megalosauroidea. Carrano et al. (2012) even found it to be a coelurosaur.

The holotype material of L. antunesi.
Paleobiology

Fossilized embryonic bones referred to L. antunesi.
The holotype was estimated at being 4,5 metres long. However, being 4 years when it died, it was a sub-adult. The size of an adult individual was estimated at around 8 metres long, which would make Lourinhanosaurus a big theropod (for Jurassic standards), but still well inside the size range observed in other Jurassic theropods. What is most surprising, however, is the presence of Gastroliths in association with the Lourinhanosaurus remains. This wouldn't be strange if the animal in question was a herbivore. The fact that these gastroliths were found inside a carnivore made paleontologists really confused.
One possible explanation is that Lourinhanosaurus was a specialized hunter, eating , for example, shellfish and crustaceans. At the time, the sea levels were much higher and Europe was more like a giant archipelago, instead of a single big land mass. It is possible that young Lourinhanosaurus lived more in coastal ecosystems and, therefore, would have different food sources, according to their ages. This way, they would not compete with older Lourinhanosaurus and even other predators, such as Allosaurus.

Lourinhanosaurus at the Museu da Lourinhã.
When younger and smaller, Lourinhanosaurus may have frequented coastal environments which were far more extensive in Jurassic Europe. Here they would be able to feed by either hunting smaller dinosaurs or raiding tidal pools for fish and crustaceans, the latter two choices requiring the use of gastroliths. Lourinhanosaurus that survived to adulthood may have grown too large to support themselves by this and switched to a greater reliance upon hunting other dinosaurs, again the two generations avoiding competition with one another for the same resources.

A juvenile Tyrannosaurus rex. (Note the more gracile and slender look of a young T. rex, comparing with an adult, which is far more bulkier).
This strategy is also seen in Tyrannosaurs. When young, they seem to have been very fast and agile predators, making them suitable to chase down smaller and faster ornithopod dinosaurs. In later life, they grew much bigger and no longer had the agility to hunt these swifter dinosaurs which also no longer offered a sufficient return in calories, so the adults switched to hunting larger and heavier dinosaurs. This niche specialisation also allowed juveniles and adults of the same species to coexist in the same ecosystem without competing with each other for the same food.
In popular culture

An early design of Jurassic Park III's logo featuring a skeleton similar in appearance to the fossil Lourinhanosaurus embryo.
- Several unused early designs of the logo for Jurassic Park III (then titled Jurassic Park: Extinction) feature the skeleton of a dinosaur embryo that closely resembles the fossil embryo of Lourinhanosaurus.



